This page may cause lag to those using devices with low RAM or bad internet.
Be careful scrolling quickly, as your device may freeze or crash.
These reasons may also make editing difficult.
This page currently is 23,452 bytes in size.
The page/section is undergoing one because some sections of the page are worded strangely. To discuss your opinion about the rewrite, see this talk page.
Do not remove this tag until the discussion has been resolved.
Earth is the third planet from the Sun. It is the only planet known to support life. Liquid water makes up 71% of Earth's entire surface, and only 29% is solid land. Earth is the largest terrestrial planet and is the fifth largest planet, with the fifth largest natural satellite. It is home to a sapient race of organisms referred to as Modern Humans, or Homo Sapiens scientifically. They have a population of about ~8,092,000,000 and are currently causing an ongoing period of geographic mass extinction and possible overpopulation on Earth.
Formation and History
The oldest material found in the Solar System is dated to 4.5682+0.0002. In theory, a solar nebula partitions a volume out of a molecular cloud by gravitational collapse, which begins to spin and flatten into a circumstellar disk, and then the planets grow out of that disk with the Sun. A nebula contains gas, ice grains, and dust (including primordial nuclides). According to nebular theory, planetesimals formed by accretion, with the primordial Earth being estimated as likely taking anywhere from 70 to 100 million years to form.
The Earth formed from a clump of rocky materials and particles about 4.58 billion years ago. It was a molten planet with extreme volcanic activity and had an atmosphere composed mostly of hydrogen and helium, similar to that of the Sun and Jovians' atmosphere composition.
Around 4.53 billion years ago, a massive Earth trojan planet referred to as Theia, came in an unstable orbit around Earth and caused a catastophic collision event. This collision completely obliterated Theia and ripped off Earth's outer crust, throwing back the leftover debris into a planetary ring system, like Saturn. The ring system later clumped together into a molten ball of rock and debris which would be now known as the Moon.
As the molten outer layer of Earth cooled it formed the first solid crust, which is thought to have been mafic in composition. The first continental crust, which was more felsic in composition, formed by the partial melting of this mafic crust. The presence of grains of the mineral zircon of Hadean age in Eoarchean sedimentary rocks suggests that at least some felsic crust existed as early as 4.4 Ga, only 140 Ma after Earth's formation. There are two main models of how this initial small volume of continental crust evolved to reach its current abundance. The two models and the data that support them can be reconciled by large-scale recycling of the continental crust, particularly during the early stages of Earth's history.
Ice Ages
There have been at least five major ice ages in Earth's history (the Huronian, Cryogenian, Andean-Saharan, late Paleozoic, and the latest Quaternary Ice Age). Outside these ages, Earth seems to have been ice-free even in high latitudes; such periods are known as greenhouse periods.
The most recent pattern of ice ages began about 40 Million years ago, and then intensified during the Pleistocene about 3 Mya.
Earth's Sister Planet (Venus)
Venus, the Earth's neighboring planet, is nicknamed as its sister due to its similar size and shape. However, they're very different from each other. Venus has ongoing volcanic activity and a thick atmosphere which traps heat on the surface, making a catastrophic greenhouse effect on the entire planet and making life impossible. Earth, on the other hand, is 70.6% water and has an atmosphere of oxygen and nitrogen, unlike Venus.

Earth’s atmosphere. Clouds are visible at the bottom.
Atmosphere
The Earth's atmosphere is mostly made of nitrogen. In fact, more than three fourths of the atmosphere is nitrogen. Oxygen makes up just more than one-fourth of the atmosphere. The rest is made up of less than one percent argon and carbon dioxide.
The atmosphere is split into two main layers: the troposphere and the stratosphere. The troposphere is the closest layer of the atmosphere to us. All of the weather on Earth occurs in this layer. The stratosphere is the lowest layer of the mesosphere, and is where the temperature of the atmosphere begins to increase due to the absorption of ultraviolet radiation from the Sun. This layer is also rich with ozone, for it contains a portion of the ozone layer.
Other layers include the mesosphere, the region in the atmosphere at which the temperatures drop to below -100 degrees Fahrenheit due to radiation being reflected away from this layer into the stratosphere. This layer is where the majority of the ozone layer is found. The ozone layer is the layer created by the build up of ozone, which is a gaseous substance that absorbs most of the ultraviolet radiation from the Sun.
Clouds are another addition in the atmosphere. These occur when air in the troposphere begins to rise and then fall. The cool air falls since it is more dense and the warm air rises because it is less dense. This process is called convection. When water vapor rises, it becomes heated and continues rising because it becomes less dense. Then, once it rises above the clouds, it cools and condenses, becoming clouds.
Life on Earth
Earth is the only known planet in the entire universe to have life. there are some habitable planet candidates outside of our solar system called extrasolar planets, or exoplanets for short. Although Homo sapiens (Humans) are the only known intelligent species as of right now, it is still more than likely possible that there is life outside of our solar system somewhere, or maybe even inside of our solar system. But we will have to go to other planets to know for sure though. some notable life on the planet Earth are pigs, humans, dogs, cats, cows, sheep, and rabbits.
The first life that was able to develop on earth, was most likely around more than 3 billion years ago, when the sun was still warming up in the solar system is still quite chaotic place. Over a period of billions and billions of years, life became more intelligent, and they went from a single celled organisms to multi celled organisms. Although there is some hardships along the way, like multiple mass extinctions, like for the dinosaurs which were obliterated by a comet, as of right now the most dominant species on the planet of earth, are the Homo sapiens otherwise known as humans commonly. Some humans pollute the atmosphere of the Earth, and it may come back to them one day as a mass extinction. Humans are also one of the main causes of the catastrophe that is global warming. As of 2023, humans continue to become more intelligent, although this has been setback by multiple factors.
Humanity
This article/section may/may not contain informal or personal opinions. If said page/section does contain these, refer to the Wiki Policy or Article Guidelines on how to correct.
The page/section is undergoing one because some sections of the page are worded strangely. To discuss your opinion about the rewrite, see this talk page.
Do not remove this tag until the discussion has been resolved.
Humans are the most dominant species on Earth right now. They have created separate countries, and even began exploration of outer space. Although they do not work together that much, sometimes humans do wars, which is when a country and another country start fighting each other over something. Nuclear weapons have been created as a weapon of war against other countries, and can create large impacts if used. Thankfully, the use of them is very limited, and a nuke has only ever been used two times against another country. Human activities have impacted Earth's environments. Through activities such as the burning of fossil fuels, humans have been increasing the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, altering Earth's environment and climate. Humanity's current impact on Earth's climate and biosphere is unsustainable, threatening the livelihood of humans and many other forms of life.
Features
The page/section is undergoing one because some sections of the page are worded strangely. To discuss your opinion about the rewrite, see this talk page.
Do not remove this tag until the discussion has been resolved.

An image of a human smiling.
This text serves as a description of humans. Their body can be divided into head, torso, legs and arms. The head is the control lever of the entire body; it can think, see, hear, smell and feel. Arms are there to grab things, hold them and to write and draw. Humans can run and walk with their legs. Furthermore, legs stabilize the body so a human doesn't just collapse to the ground. In addition to the head, the torso is also very important because it contains very important organs, the heart, the lung and the liver. Humans are also surrounded by a layer named "skin". The color of that skin is not always the same, some humans have darker skin while some have lighter skin. This skin is however only visible when you look at a human's head or arm, as humans are known to cover most of their body with textile. This textile has been named "clothing" by humans and is now a crucial part of the basic equipment.
Advancements
These are the major advancements of humanity:
- 20000 BC: Invention of pottery
- 15000 BC: Invention of agriculture
- 5000 BC: Invention of the wheel
- 500 BC: Invention of democracy
- 100 BC: Invention of plumbing
- 850: Invention of gunpowder
- 1550: Renaissance
- 1850: Industrial Revolution
- 1800: Invention of the train
- 1880: Invention of the lightbulb
- 1876: Invention of the telephone
- 1886: Invention of the car
- 1896: Invention of the radio
- 1927: Invention of television
- 1940: Invention of the computer
- 1945: Invention of the nuclear bomb
- 1975: Invention of the personal computer
- 1991: Invention of the Internet
- 2010: Invention of smartphones
Nations
The page/section is undergoing one because some sections of the page are worded strangely. To discuss your opinion about the rewrite, see this talk page.
Do not remove this tag until the discussion has been resolved.
Humans divide their planet by nations. Each nation has their own system, culture and history. Some well-known nations include:
- USA
- China
- Russia
- India
- Japan
- Germany
- UK
- Turkiye
- France
- Canada
- Australia
- Indonesia
- South Korea
- Iran
- Italy
- Spain
- North Korea
- Brazil
- South Africa
Space Exploration
This page/section is done in an irregular style or format than is usual. Please fix this by editing it
Humans have been doing space exploration for a while now. It started in the 1950s and it has gotten more expensive since. The planets that have been visited by humans doing space exploration have been Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. Other dwarf planets like Haumea and Eris have been up for possible probe mission ideas. Humans have thought about exploring outside of our solar system, with space telescopes, and some people have even hypothesized possible space probes that could fly to other solar systems in possibly under 100 years! Sadly, that feat is going to take a while to achieve, but it might happen someday. Some humans have even proposed exploring outside of the Galaxy!
Extinctions
The page/section is undergoing one because some sections of the page are worded strangely. To discuss your opinion about the rewrite, see this talk page.
Do not remove this tag until the discussion has been resolved.
This page/section is done in an irregular style or format than is usual. Please fix this by editing it
With life, comes extinctions. Extinctions are when a species dies out, like the Dodo Bird, there is no more of the species left to reproduce, usually caused by climate change or the presence of humans hunting for sport and food.
Mass extinctions
An extinction event is a widespread and rapid decrease in the biodiversity on Earth. Such an event is identified by a sharp change in the diversity and abundance of multicellular organisms. It occurs when the rate of extinction increases with respect to the background extinction rate.
List of mass extinctions
| Date | Probable causes |
|---|---|
| Holocene Exctinction | ~10,000 ya to current |
| Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event | 65 mya |
| Triassic-Jurrasic extinction event | 201 mya |
| Permian-Triassic extinction event | 252 mya |
| Kellwaser Event | 372 mya |
| Late ordovician mass extinction | 445-444 mya |
List of Nuclear weapon Usages
| Date Used | Country Used By | Country Used On | Name Of War Used In |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1945 | United States | Japan | World War II |
| 1945 | United States | Japan | World War II |
Space Exploration
This page/section is done in an irregular style or format than is usual. Please fix this by editing it
Humans have been doing space exploration for a while now. It started in the 1950s and it has gotten more advance ever since. The planets that have been visited by humans doing space exploration have been Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. other dwarf planets like Haumea and Eris have been up for possible probe mission ideas. humans have thought about exploring outside of our solar system, with space telescopes, and some people have even hypothesized possible space probes that could fly to other solar systems in possibly under 100 years! Sadly, that feat is going to take a while to achieve, but it might happen someday. Some humans have even proposed exploring outside of the Solar System with probes designed to be propelled by lasers.

Artist’s illustration of a Habitable/Terraformed Mars. Mars may have been habitable in the past.
Terraforming Mars
Humans have been proposing to terraforming the planet Mars. It is currently unknown how it might be done, but it could be achieved. Although Mars is a barren wasteland today, it could be a thriving place for humanity in the next centuries.
Global warming
The page/section is undergoing one because some sections of the page are worded strangely. To discuss your opinion about the rewrite, see this talk page.
Do not remove this tag until the discussion has been resolved.
Global warming is a catastrophe that is caused by many reasons, but most people blame it on themselves, Homo sapiens. Global warming is making the atmosphere and oceans hotter making the ice caps start to melt around the world. This is causing the extinction of some animals, and the pollution of the atmosphere of Earth. Global warming is not good at all and it should be stopped, although it might be too late by now.
However, in the previous years, progress on this issue has been made by humans. Energy is slowly turning green and new technologies such as artificial meat and carbon capture are also getting more advanced year by year. Still, this might be not enough to save Earth from catastrophe.
Tectonic Plates

Interior of the Earth.
Tectonic plates are the makeup of the lithosphere. These plates can be 60 km thick and are the plates that drive the continents. These plates can join together to form boundaries. Some boundaries can cause geographical features such as mountains when they collide and push up the crust plate (convergent boundary], some can cause earthquakes when they slide against each other causing tension (transform boundary), or seafloor spreading when two plates move away from one another (divergent boundary).

Map of the Tectonic Plates on Earth.
Due to this, there is a process called continental drift. Continental drift was founded by Alfred Wegener, and involves all of the continents moving about the Earth, but the change is so small, it is undetectable by humans. This theory proves that Pangaea existed more than 250 million years ago. (Pangea Sub Section)
Pangea
Pangaea was a supercontinent that combined all of the known continents we know today. Through the process of continental drift, Pangaea split up after going through several changes and shifted into the places the continents are in today.
Continents
Continents were created from continental drift. There are 7 current ones, named North America, South America, Europa, Africa, Asia, Oceania, and Antarctica. sometimes continents are grouped into larger ones, like America, and Eurasia.

The magnetic field of Earth. It protects Earth from solar radiation and flares.
Magnetic Field
The main part of Earth's magnetic field is generated in the core, the site of a dynamo process that converts the kinetic energy of thermally and compositionally driven convection into electrical and magnetic field energy. The field extends outwards from the core, through the mantle, and up to Earth's surface, where it is, approximately, a dipole. The poles of the dipole are located close to Earth's geographic poles. At the equator of the magnetic field, the magnetic-field strength at the surface is 3.05×10−5 T, with a magnetic dipole moment of 7.79×1022 Am2 at epoch 2000, decreasing nearly 6% per century (although it still remains stronger than its long time average). The convection movements in the core are chaotic; the magnetic poles drift and periodically change alignment. This causes secular variation of the main field and field reversals at irregular intervals averaging a few times every million years. The most recent reversal occurred approximately 700,000 years ago. The extent of Earth's magnetic field in space defines the magnetosphere. Ions and electrons of the solar wind are deflected by the magnetosphere; solar wind pressure compresses the dayside of the magnetosphere, to about 10 Earth radii, and extends the nightside magnetosphere into a long tail.Because the velocity of the solar wind is greater than the speed at which waves propagate through the solar wind, a supersonic bow shock precedes the dayside magnetosphere within the solar wind.Charged particles are contained within the magnetosphere; the plasmasphere is defined by low-energy particles that essentially follow magnetic field lines as Earth rotates. The ring current is defined by medium-energy particles that drift relative to the geomagnetic field, but with paths that are still dominated by the magnetic field, and the Van Allen radiation belts are formed by high-energy particles whose motion is essentially random, but contained in the magnetosphere. During magnetic storms and substorms, charged particles can be deflected from the outer magnetosphere and especially the magnetotail, directed along field lines into Earth's ionosphere, where atmospheric atoms can be excited and ionized, causing the aurora.
Natural Resources
Earth has resources that have been exploited by humans. Those termed non-renewable resources, such as fossil fuels, are only replenished over geological timescales. Large deposits of fossil fuels are obtained from Earth's crust, consisting of coal, petroleum, and natural gas. These deposits are used by humans both for energy production and as feedstock for chemical production. Mineral ore bodies have also been formed within the crust through a process of ore genesis, resulting from actions of magmatism, erosion, and plate tectonics. These metals and other elements are extracted by mining, a process which often brings environmental and health damage.
This is the composition of Earth's crust, rich in materials and often looted by humanity:
- Oxygen - 46.1%
- Silicon - 28.2%
- Aluminum - 8.23%
- Iron - 5.63%
- Calcium - 4.15%
- Sodium - 2.36%
- Magnesium - 2.33%
- Potassium - 2.09%
- Titanium - 0.57%
- Hydrogen - 0.14%
- Phosphorus - 0.10%
Orbit and Rotation
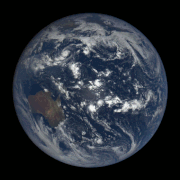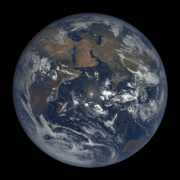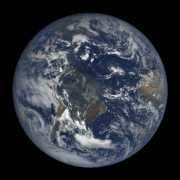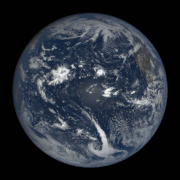
Gif of the Earth’s rotation, taken by a satellite.
Earth's orbit takes one solar year. This is equal to 365.256 sidereal (with respect to the stars) days, usually rounded to 365. The extra one-fourth on the year, every four years, the one-fourth becomes a whole and adds an extra sidereal Day, making it a leap year, making it 366 days.
Earth takes 23 hours, 57 minutes to make one rotation on its axis. This number is mostly rounded to what we know as 24 hours in one Earthen day.
Seasons

A diagram of the different seasons.
There are four seasons. Winter, spring, summer, and autumn. Winter is the coldest season, while summer is the hottest. Spring and autumn are in between. If it is summer in the northern hemisphere, it is winter in the southern hemisphere, and vice versa. Winter lasts from December 21 to March 21, Spring lasts from March 21 to June 21, Summer lasts from June 21 to September 21, and Fall (Autumn) lasts from September 21 to December 21.
Moons
Earth has one permanent moon, which is the Moon , but it occasionally captures nearby asteroids thus becoming temporary natural satellites. Some of the only observed examples were 2006 2H120, and 2020 CD3. Earth also a few some quasi-satellites.
Future
As the future goes on, the Earth’s atmosphere will probably continue to get more polluted and polluted, and more extinctions will happen. Humans may get more advanced. Over the next 1.1 billion years, solar luminosity will increase by 10%, and over the next 3.5 billion years by 40%. overpopulation on the planet by humans will probably continue to rise, unless it’s some humans decide to terraform and go to Venus, Mars the Galilean Moons, Titan, or Enceladus. If not, by 2090, the earth’s population will be greater than 11 billion people. Earth will continue to get warmer and warmer until the plants start to die of heat by the sun’s increasing brightness, and the humans will most likely move away. This has something to do with the next subsection.
The Sun’s Red Giant Phase
Onwards, around beyond 1 billion years from now, the sun will exit its main sequence stage, and start to fuse new elements. It will begin to expand in soon and we will expand into around the orbit of Earth. It is currently unknown if the sun will, or will not engulf the planet Earth. if it does, will probably not exist anymore after the sun explodes and becomes a white dwarf. If it isn’t, after the sun becomes a white dwarf, it will get closer and closer to the white dwarf star until it collides in the far far future. The current projected path is not know yet. when the sun becomes a white dwarf, Earth, might get destroyed or lose a lot of it’s mass by the blast of materials, unless the death of stellar objects not capable of supernovae turns out to be less violent as we expect.
Far Far Future
As added in the last section, Earth might collide with the now white dwarf Sol in the far far future. This period of time is very obscure and very little is known about it.
Sources and Links
- https://www.nationalgeographic.com/science/article/earth
- https://www.space.com/54-earth-history-composition-and-atmosphere.html
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JGXi_9A__Vc
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Earth
Gallery
See Also
| The Planets and Dwarf Planets | |
|---|---|
| Planets | |
| Mercury • Venus • Earth • Mars • Jupiter • Saturn • Uranus • Neptune | |
| Dwarf Planets | |
| Ceres • Pluto • Haumea • Makemake • Quaoar • Eris | |
